GI and Laparoscopic Surgery
GI Surgery
GI surgery also known as gastrointestinal surgery deals with all the parts of gastrointestinal tract. It includes all cancer and benign condition of esophagus, stomach, liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, small and large intestine.
Minimal access surgery today has become a gold standard for treatment of many abdominal problems. Laparoscopy is a low risk, minimally invasive procedures and the advantages include fast recovery, less post-operative pain, minimal and cosmetic incision. Less blood loss, minimum post- surgery stays in hospital and easy return to daily routine.
Oesophagus
Oesophageal SurgeryVarious conditions require oesophageal surgery. Surgery is done when the non-invasive methods of treatment fail to provide adequate relief to the patient or in cases where surgery is the only option left to save the patient's life or provide relief from symptoms. Various conditions that require oesophageal surgery include Achalasia, Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Corrossive esophageal stricture, Hiatal Hernia, Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia, oesophageal cancer, and in advanced stage achalasia.
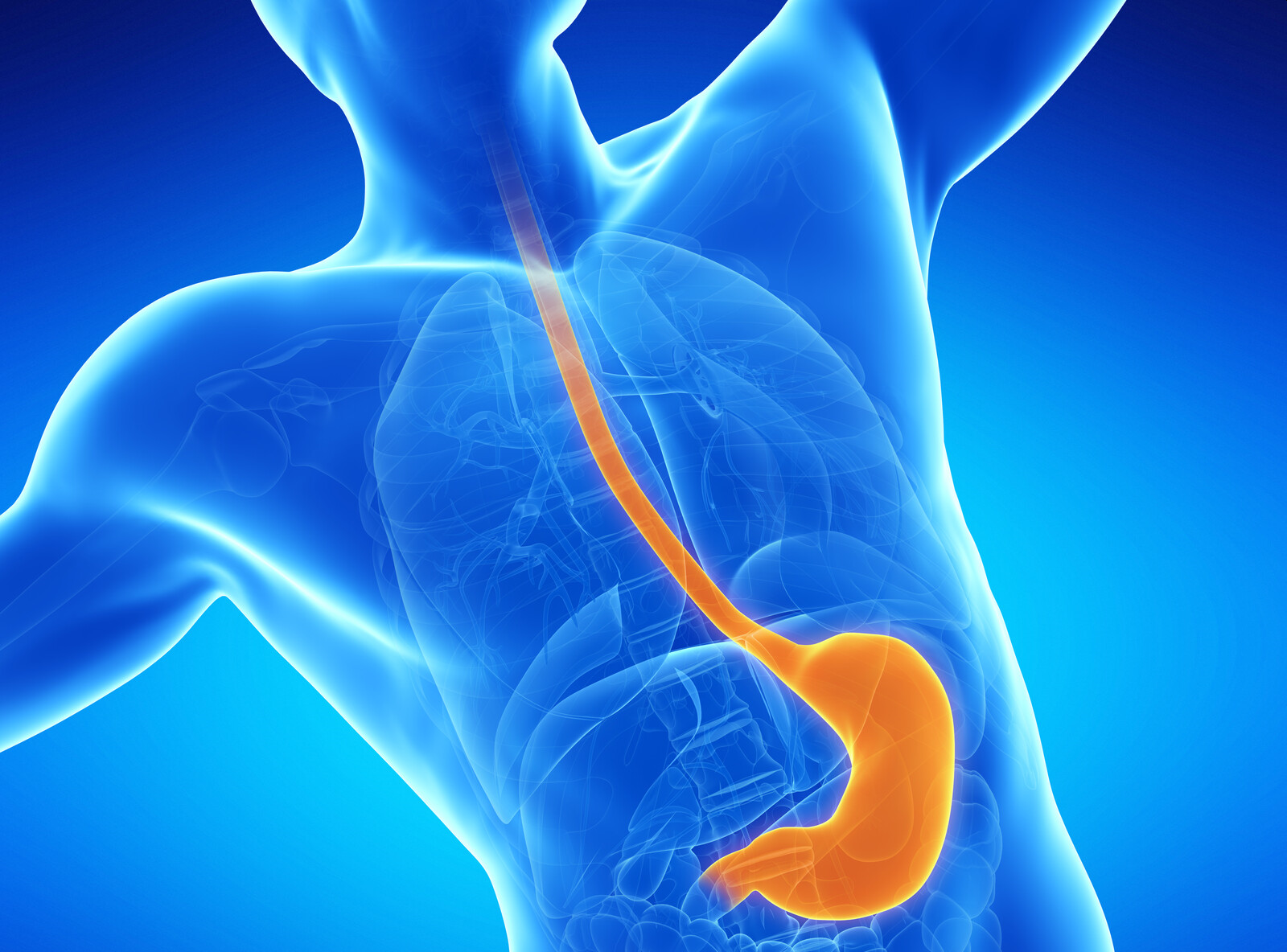
What Is Achalasia?
Achalasia is the condition characterized by difficulty in passing the food or fluid from the mouth to stomach. Nerves are present in the esophagus that regulates the flow of fluid and food from the mouth to stomach by contracting and relaxing the muscles. Further, the lower oesophageal sphincter also relaxes to allow the food to move into the stomach. In achalasia, the nerves of the esophagus get damaged leading to improper transit of food and fluid in the stomach.
How The Diagnosis And Treatment Of Achalasia Are Done?
Most of the symptoms of achalasia are like digestive disorder thus increases the risk of its misdiagnosis. Various diagnostic methods such as oesophageal manometry, upper endoscopy, and X-ray of the digestive system is done to diagnose achalasia. There is no treatment for this disease and the treatment is directed to provide relief from symptoms. Non-invasive treatment includes medication and pneumatic dilation. Surgery is also done in cases when non-invasive treatment is ineffective. Various surgical options for achalasia include Peroral endoscopic myotomy, Heller myotomy, and Fundoplication.
What Is Hiatus Hernia?
A large muscle separates the abdomen and diaphragm. Through the diaphragm, at a point called hiatus, the esophagus passes and connects to the stomach. A hiatus hernia occurs when the stomach is pushed up. This causes a bulging of the stomach. Mild hiatus hernia is not a cause of concern and is diagnosed when the abdomen is evaluated for any other reason. However, the large hiatal hernia poses a problem and may lead to heartburn as the food and other substances move upward into the esophagus.
What Are The Treatment Options For Hiatus Hernia?
Non-invasive treatment options for hiatus hernia are aimed to provide relief from the symptoms such as heartburn or acidity. Medications may include antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and H2 receptor blocker. Surgery is required in severe cases of hiatus hernia. Surgery includes removing the hernia sac, reforming the sphincter, and pulling the stomach back into the abdominal cavity.
What Are The Causes For Oesophageal Cancer?
Oesophageal cancer is the cancer of esophagus which usually initiates in the inner lining of the esophagus. Men are more prone to develop oesophageal cancer as compared to women. The exact cause of oesophageal cancer remains unknown. Various factors increase the risk of oesophageal cancer. These include smoking, obesity, drinking alcohol, achalasia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, making habit of drinking the hot liquid, lack of fruits and vegetables in the diet, and presence of Barrett's esophagus.
What Are The Various Treatment Options For Oesophageal Cancer?
Surgery is one of the options for treating oesophageal cancer. Surgery of esophagus is done either to remove small tumors, to remove part of the esophagus or to remove complete esophagus and upper part of the stomach depending upon the severity of the disease. Other options for treating oesophageal cancer include chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Different options may be used simultaneously for treating oesophageal cancer.
Stomach
Stomach SurgeryStomach surgery is required in the condition which is not treated with non-invasive treatment options available. Stomach acid disease, when not treated with conservative, non-invasive means may require surgery. Removal of the stomach is a standard treatment in the management of stomach cancer. Other diseases which require stomach surgery include gastroparesis, and dysphagia.
What Is Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer is the formation of cancerous cells in the stomach lining. Stomach cancer is also known as gastric cancer. The condition may occur at any part of the stomach. Patients with stomach cancer experience indigestion and pain in the stomach. Although the sixth most common cancer all over the world, it is third in claiming lives due to cancer.
Whar Are The Causes Of Stomach Cancer?
Although the definite cause of cancer is not known, various factors increase the risk of stomach cancer. Male is twice at more risk of developing stomach cancer as compared to female. It is believed that estrogen present in female protect them against this cancer. The risk factors include:
- H. pylori infection
- Incorporation of smoked food, processed meat, red meat, and pickled vegetables may increase the risk of stomach cancer. Although the connection between food and the risk of stomach cancer is weak, it is best to take a healthy diet which includes fresh fruits.
- Genetics
- Chronic atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia
What Are The Treatment Options For Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer can be managed through medications, radiotherapy, and surgery. The treatment strategy is based on the stage and severity of the disease. Medications include chemotherapy, targeted medications, and immunotherapy. Surgical options for stomach cancer include Subtotal gastrectomy in which a portion of the stomach is removed, Total gastrectomy, and Endoscopic mucosal resection. Now a day’s these surgeries can be done through laparoscopic methods (Key Hole surgery) also.
Colorectal
Colorectal SurgeryWhat Is Colorectal Surgery?
Colorectal surgery is the surgical intervention required to treat the condition related to colon, anus, and rectum. Although the preferred treatment is largely non-invasive when such treatment did not alleviate the symptoms, surgery is required. Proctology is another less commonly used term for colorectal disorders and is generally used to describe the disorders related to anus and rectum. Colorectal surgery also includes diagnosis of the disease-related to colon, anus, and rectum for example colonoscopy.
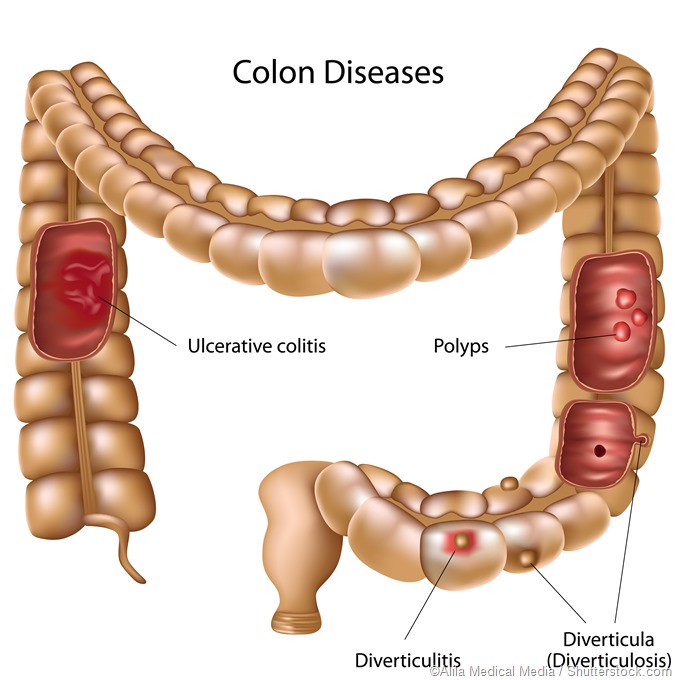
Which Conditions Require Colorectal Surgery?
Various conditions require colorectal surgery such as:
- Anal fissures
- Hemorrhoids
- Severe constipation
- Rectal prolapse
- Ileocaecal Tuberculosis
- Colon cancer
- Rectal cancer
- Congenital conditions such as imperforate anus
- Fecal incontinence
- Intestinal obstruction
- Anal injury
- Fistula
What Is Intestinal Obstruction?
Intestinal obstruction is the condition that causes blockage of the food from passing through the small or large intestine. If left untreated, intestinal obstruction may lead to serious complications due to damage of blocked part. The condition may be caused due to post-surgical complications including the formation of fibrous bands, infection in intestine, inflammation, tuberculosis and cancer. The patient suffering from intestinal obstruction experiences constipation, vomiting, loss of appetite, and abdominal swelling. Diagnosis of the condition is done through physical examination, imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan and X-ray, and barium enema may also be used for colon imaging.
How Surgery Helps In Treating Intestinal Obstruction?
When the other methods for treating the condition is not successful, surgery is done for removing the intestinal obstruction. Early laparotomy is done to treat complete bowel obstruction. Fluid status should be monitored in a patient with severe dehydration before surgery. Apart from removing the obstruction, the surgery should also ensure to avoid the risk of obstruction in future such as hernial repair, lysis of fibrous bands and elimination of foreign bodies. Enterotomy is done to remove the obstruction caused due to gallstone.
What Is Colorectal Cancer?
Cancer that develops in colon and rectum is known as colorectal cancer or bowel cancer. The condition is further divided into colon cancer or rectal cancer depending upon the specific position of cancerous cells or tumor. Women are slightly at risk of developing this cancer as compared to men and is the second-highest cause for cancer death in women. The patient suffering from colorectal cancer experiences blood from the rectum, abdominal pain and bloating, change in bowel habits, diarrhea or constipation, blood in stools, and unexplained weight loss.
What Are The Treatment Options For Colorectal Cancer?
Treatment options for colorectal cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and ablation. Surgery for colon cancer includes polypectomy, which involves the removal of cancer as a polyp, and local incision that involves the removal of cancer lesions along with surrounding tissues. In some cases, colectomy is recommended which involves the removal of either partial or complete colon. Colectomy is done either through open colectomy or Laparoscopic-assisted colectomy. Surgery for rectal cancer includes Transanal endoscopic microsurgery, Low anterior resection, Proctectomy with colo-anal anastomosis, and Abdominoperineal resection.
What Is Rectal Prolapse?
The rectum is the terminal part of the large intestine. It stores the feces before being passed out. When the rectum protrudes from the anus, the condition is termed as rectal prolapse. Various types of rectal prolapse include internal, mucosal and full-thickness rectal prolapse. Pregnancy, constipation, and diarrhea increase the risk of rectal prolapse. In the case of internal prolapse, when the rectum does not protrude out, the patient experiences blood from rectum, constipation, and discomfort.
How Rectal Prolapse Treated Through Surgery?
Surgery is done to place the rectum back in the original position. Various rectal prolapse surgeries are available depending upon the condition of the patient. You doctor will decide the surgery that best treats your condition. Various types of rectal prolapse surgeries include perineal rectosigmoidectomy, Laparoscopic rectal prolapse surgery, and repairing of rectal prolapse through the abdomen.
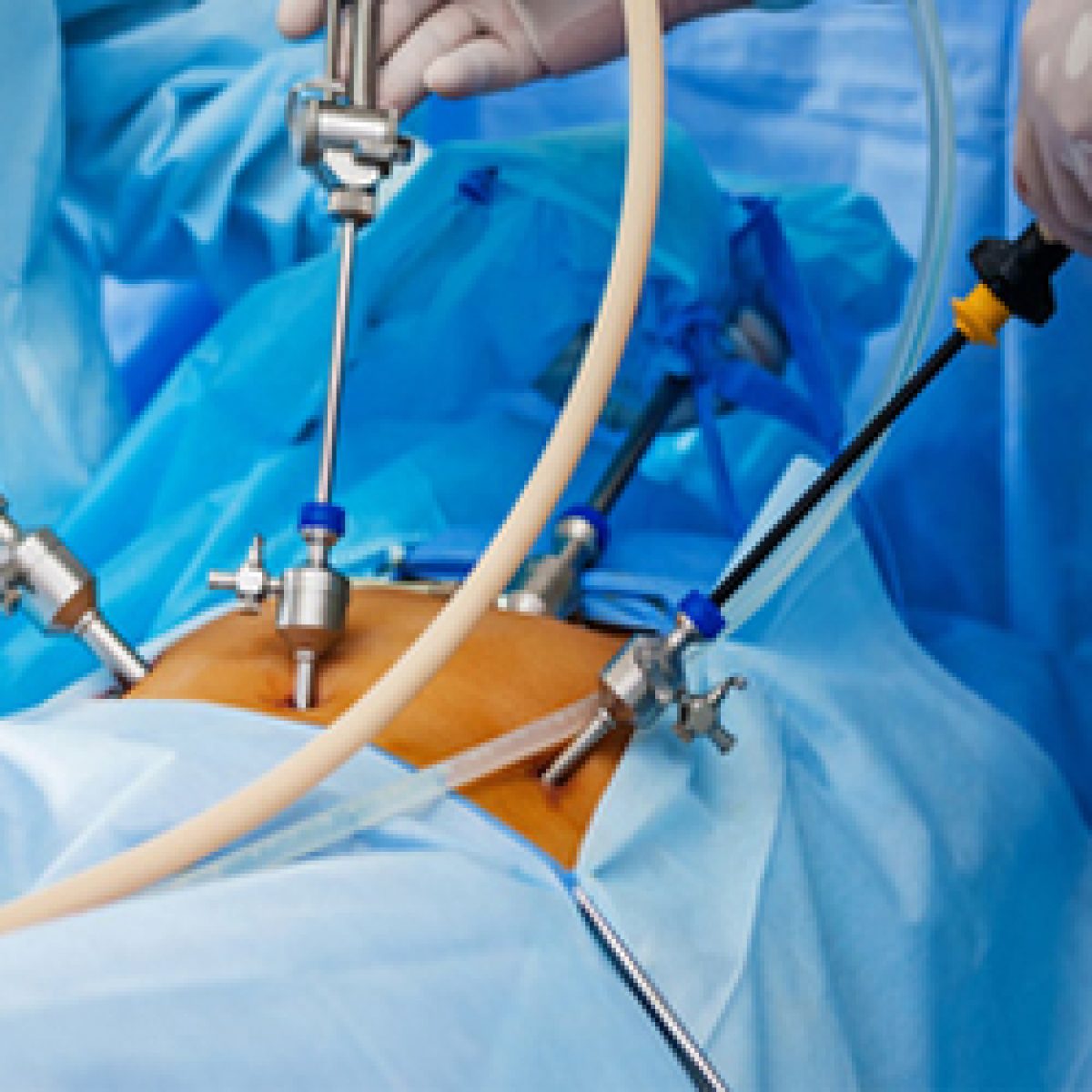
Laparoscopic Surgery
What Is Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is an advanced surgical process with significant benefits to the patients. Currently, most surgery, as far as possible, is done through this method of surgery. The other names for this surgery are minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery. The laparoscopic surgeries are safe and with the advancement in technology and evolution of more sophisticated techniques, the outcomes of these surgeries favourable most of the time. During the minimally invasive surgery or laparoscopic surgery, few small cuts are made. From one cut, a tube along with the camera are inserted that provides information related o the surgical site. From another cut, a special type of instrument is inserted through which the surgeons perform surgery.
What Are The Benefits Of Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery provides ample advantages to the patient as well as surgeons.
These includes:
Smaller incision: Very small incisions are made at the site of surgery. The size of the incision is such that a small tube and small size instrument pass through from it.
Less pain: The patient who has undergone laparoscopic surgery have less discomfort and less pain.
Quick wound healing: As the incision is very small, the wound healing after surgery is quite fast. The risk of infection in laparoscopic surgery is quite low.
Fast recovery time: The length of time for hospital stay gets significantly reduced and the time of recovery is fast.
Less internal scars: Due to reduced bleeding and small incisions, the patient is at least at risk for developing the internal scars.
What Are The Risks Of Laparoscopic Surgery?
As this is also a surgical process, thus carries the risk of surgery. The risk further increases if the patient has underlying medical conditions. The various risk associated with laparoscopic surgery includes bleeding, infection, clotting, damage to internal structures such as blood vessels and side effects of anesthesia.
How Laparoscopic Surgery Is Different From Open Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is different from open surgeries on various parameters. With the open surgery, the surgeon has to create a long cut to expose the site of surgery which is reduced to 3-4 small incisions with laparoscopic surgeries. Due to small incision, the wound healing and rate of recovery is fast as compared to open surgery. Small body tissue is exposed to the external environment, thus having less chance of infection as compared to open surgery.
Can Laparoscopic Surgery May Be Done For Cancer?
Laparoscopic surgery is also done to remove the tumor. The surgical outcomes of laparoscopic surgery for cancer are similar to open surgeries.
