Liver Surgery
Hepatectomy (Liver Resection)
Hepatectomy or liver resection is a surgical operation to remove part or all of your liver. If you have part of your liver removed, it can grow back to its former size. If you have a total hepatectomy, you will need a liver transplant.
OVERVIEW
What is a liver resection (hepatectomy)?
A liver resection, or hepatectomy, is a surgical procedure to remove part of your liver. You can have up to two-thirds of your liver removed as long as the rest of your liver is healthy. If you have liver disease, a smaller portion may be removed. Your liver can grow back. If your remaining liver is healthy, it’ll grow back to its former size.
Why is liver resection performed?
You may have a liver resection to treat liver disease, or when you want to donate part of your liver for living donor liver transplantation.
Causes of disease that may require hepatectomy
Surgeons mostly perform a partial liver resection to remove a cancerous, precancerous or benign (noncancerous) tumor. Liver cancer can be primary — which means that it originates in the liver — or it can be secondary, which means that it originates in another organ and spreads.
The most common liver cancers treated by partial hepatectomy include:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (primary liver cancer).
- Cholangiocarcinoma (primary liver cancer).
- Metastatic colorectal cancer (secondary liver cancer).
Other benign lesions include:
- Gallstones in the intrahepatic ducts — the bile ducts inside your liver.
- Adenoma (primary benign tumor).
- If they cause symptoms, liver cystadenoma or a cyst.
Liver resection for living donor liver transplant
You may also have a partial liver resection as a living liver donor. This operation removes a portion of your healthy liver to donate to someone who needs a liver transplant. Both your remaining liver part and your transplanted liver part will grow back into a full-sized liver.
How serious is a liver resection?
Liver resection is considered a technically difficult surgery. One reason is that your liver has many vessels in it and may bleed a lot, so liver surgeons have to be trained in special techniques to not injure the vessels and to manage any bleeding. When your resection is smaller (less than half of your liver), it’s less risky and can be done through minimally-invasive surgery techniques, such as laparoscopy or robotic surgery. When you need a major resection (more than half of your liver), it becomes more dangerous and difficult. As a rule, you want to have your liver resection with experienced specialists because of the complexity of the operation.
PROCEDURE DETAILS
What happens before a liver resection?
Your healthcare provider will need to determine whether surgery is the best option to treat your condition. This may depend on:
- Whether you’re healthy enough to tolerate surgery.
- Whether the lesion in your liver is technically operable.
- Whether you have cancer in other parts of your body besides your liver.
In some cases, radiation therapy, interventional radiology or chemotherapy may be done before surgery to reduce the cancer size, make the operation easier and safer, or improve the chance of curing cancer.
Your healthcare provider will also need to decide whether a partial hepatectomy or a liver transplant is needed. This may depend on:
- How extensive the tumor is.
- How healthy your liver is.
- How much functional liver can be left after resection.
- Whether you qualify for a transplant.
To screen you for these factors, your healthcare provider may want to run some tests, including:
- Imaging tests, like a CT scan or an MRI.
- Liver function tests (blood tests) to determine how well your liver works.
- Liver biopsy.
How is a hepatectomy performed?
Hepatectomy can be performed by open, laparoscopic or robotic surgery. Your surgeon will determine the best method to manage your condition. Laparoscopic and robotic surgeries are less invasive because they’re done through smaller incisions — usually four to six small incisions, each about a half-inch in size. These smaller incisions make for an easier and quicker recovery. But traditional open surgery may be necessary to manage more extensive or complicated liver resections.
What is the difference between laparoscopic/robotic vs. open hepatectomy?
In open abdominal surgery, one long incision called a laparotomy opens up your abdominal cavity. Surgeons are able to visualize your abdomen directly. It’s best suited for more complex procedures.
In laparoscopic surgery, the entire operation takes place through small “keyhole” incisions while your surgeon looks at the images from the camera on a screen. They use specially designed, long instruments to complete your liver resection. They can also use robotic arms. Movement is somewhat restricted, so surgeons traditionally use a laparoscopic or robotic approach for less complex liver resections. But with the development of surgical techniques, more complex surgeries such as major liver resection or living donor liver resections are now possible through a laparoscopic or robotic approach.
How much liver does a partial resection remove?
The goal of partial liver resection is to remove the diseased part of your liver (with a safe margin around any cancerous tumor) while leaving enough liver behind to keep up with all the work your liver has to do. The portion of liver that needs to be left behind depends on how damaged the liver is overall. A healthy liver may be able to lose up to two-thirds of its volume and still recover. A significantly damaged liver may only be able to lose one-third.
What happens when part of your liver is removed?
Your liver has a remarkable ability to repair and regenerate itself. It wants to return to a consistent size that’s proportional to your overall body size. When liver cells detect damage, they communicate with each other to begin dividing and replicating themselves until that size is reached. This process depends on healthy liver tissue, and some livers may be slower to regenerate or reach their former size.
What are the different types of liver resections?
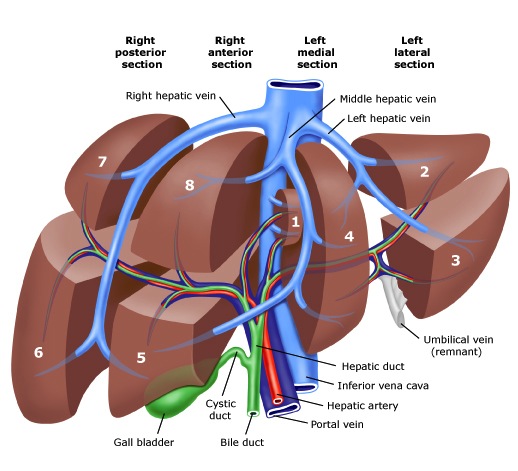
Liver resection can be classified into major and minor liver resection. Removal of more than three segments is a major resection while removing small portions is a minor resection. Examples of common surgeries include:
- Major liver resection: Right or left hepatectomy or lobectomy removes the right or left lobe (hemiliver).
- Minor liver resection: Segmental or wedge resection removes a segment or a part of a segment with a tumor with a margin around it. Another minor liver resection is the left lateral sectionectomy, which removes the lateral part (section) of the left lobe.
- Multiple liver resections: Multiple tumors may be resected at the same time. If your surgeon thinks some tumors would best be treated with ablation, they may combine resection with ablation.
- Two-stage liver resection: If your surgeon suspects it might be too dangerous to remove all the tumors in one operation, they may do the resection in two stages. The first operation removes a part of the tumor. Then, your liver regenerates for several weeks so you’ll have enough remaining liver after the second surgery, which will remove the remaining tumors.
What are the steps of the hepatectomy procedure?
There are variations to the procedure, depending on how much liver your surgeon removes and the surgical technique they use. In general, a hepatectomy follows these steps:
- You’ll be put to sleep under general anesthesia before the procedure. If you’re having open surgery, you may also have a transversus abdominis plane (TAP) nerve block, which will help with pain management after you wake up.
- If you’re having open surgery, your surgeon will make one long incision across your abdomen to open your abdominal cavity. If you’re having laparoscopic surgery, your surgeon will make 4 to 6 “keyhole” incisions, which they’ll use to place the camera (laparoscope) and surgical instruments to do the operation.
- Your surgeon will identify the section of your liver that needs to be taken out. They may use an intra-operative ultrasound to map your liver. If the section to be removed is close to your gallbladder, they may need to remove your gallbladder as well.
- Your surgeon will finely dissect your liver tissue, isolating the blood vessels and bile ducts and controlling them with metallic clips or staplers. They use ultrasonic energy devices or electrocautery devices to dissect your liver and control bleeding.
- If you’re having laparoscopic or robotic surgery, your surgeon may make an additional 2- to 5-inch incision to take the resected liver out of your body. The size of the incision depends on the size of the tumor and how much liver is removed.
How long does liver resection surgery last?
The procedure may take two to six hours, depending on the extent of the resection.
What happens after liver resection surgery?
Most people will recover in a post-anesthesia unit and then move to an in-patient room. In complex surgical cases, you may need to stay in intensive care for one or two days following the operation. You’ll have various tubes that drain fluids, decompress your stomach and give you nourishment. In intensive care, your healthcare team will closely monitor your fluid/electrolyte balance, blood glucose levels and blood loss. They’ll treat you for any abnormalities that occur.
Once you’ve stabilized, you'll continue to recover in the hospital for up to a week. You’ll gradually resume eating solid food, begin to move around more and your provider will remove the tubes. You’ll have pain medication while you recover. After discharge, you’ll make an appointment to revisit your surgeon in two weeks to check your final pathology report and discuss how you’re doing.
RISKS / BENEFITS
What are the advantages of liver resection?
As a cancer treatment, surgery has the best survival rate of all options. If the surgery successfully removes all of cancer, it can be curative. The survival rate is the same whether you have a laparoscopic, robotic or open procedure.
What are the risks or complications of liver resection surgery?
Complications may include:
- Infection. You can get an infection in your incision wound, your urinary tract or your lungs (pneumonia). Your provider treats such infections with antibiotics.
- Bleeding. Your liver has a lot of blood vessels, and it’s also responsible for making your blood clot stop bleeding. Liver surgery interferes with this process, so sometimes patients bleed too much. Some may need a blood transfusion after surgery.
- Bile leakage. Damage to any of the bile ducts in your liver during surgery can cause bile to leak, which may collect inside your abdomen. This may require placing an additional drain.
- Pleural effusion. After liver surgery, fluid can easily build up inside your chest cage. It can cause chest pain and shortness of breath. It may be treated with medication or may need to be drained.
- Ascites. Liver surgery can also cause a buildup of fluid in your abdominal cavity. It may be treated with medication or may need to be drained.
- Deep vein thrombosis. After any surgery, there’s a risk of blood clots from being in bed for a long time. Pay attention to any spot on your arms or legs that seems swollen or sore.
- Kidney failure. Sometimes surgery can cause your kidneys to stop working. It is important to stay well hydrated.
- Liver failure. If the remaining liver doesn’t have enough function left, you can go into liver failure. In this case, you may need an urgent liver transplant.
About 2% of people who have liver resection surgery die of complications. Cancer patients weigh these risks against the risks of cancer itself.
RECOVERY AND OUTLOOK
How long does it take to recover from hepatectomy?
Liver resection recovery at home takes four to eight weeks. You may need to take this time off from work. You shouldn’t try to lift anything heavy or engage in strenuous exercise while you’re recovering. It may be 12 weeks before you return to all of your normal activities.
Recovery from laparoscopic or robotic surgery is generally quicker. You’ll recover at home for about two to four weeks, but it will take six to eight weeks before you can return to your normal activities.
Getting enough protein and some gentle exercise (like walking) every day can help speed your recovery. Try to walk for at least 30 minutes each day, but rest when you need to.
What does life after liver resection surgery look like?
You’ll be sore and tired for a while. You may also feel sick to your stomach at first. These symptoms should begin to ease in the first two weeks. In the meantime, take it easy.
Your healthcare provider will give you instructions about how to care for your incision as it heals. They’ll also tell you when it’s safe to bathe and have sex again. You’ll need to avoid alcohol to protect your recovering liver.
How fast does your liver grow back after resection?
Healthy liver tissue can regenerate as much as two-thirds of its volume in as little as a few weeks. However, it’s not uncommon for it to take several months. A more damaged liver may take longer to regenerate. Factors that might affect how fast your liver regenerates include:
- Prior chemotherapy.
- Excessive fat in your liver.
- Chronic liver disease or cirrhotic livers.
What kind of scar will I have after a hepatectomy?
If you have laparoscopic surgery, you’ll have four to six small, half-inch scars, and one larger scar. If you have open surgery, you will have a long scar that’s 6 to 12 inches. It may be a horizontal scar, or it might be shaped like an “L.” It may appear red and raised above your skin but usually, the color fades over time.
WHEN TO CALL THE DOCTOR
When should I contact my healthcare provider?
Contact your healthcare provider about any usual symptoms after your hepatectomy, including:
- Bleeding or discharge from your wound.
- Persistent fever.
- Vomiting or diarrhea.
- Persistent constipation (more than three days).
- Swollen, distended abdomen.
- Jaundice (yellow eyes and skin).
